Data Interchange DSL
A general introduction and some high-level concepts for OSBP DSLs can be found in OSBP DSL Documentation.
Contents
- 1 Purpose
- 2 Overview
- 3 Data Interchange Model File
- 3.1 Package
- 3.2 Reserved Keywords
- 3.2.1 interchange
- 3.2.2 describedBy
- 3.2.3 merge
- 3.2.4 persist
- 3.2.5 remove
- 3.2.6 elementSize
- 3.2.7 file -> CSV | EDI | XML
- 3.2.8 report
- 3.2.9 delimiter
- 3.2.10 indent
- 3.2.11 quoteCharacter
- 3.2.12 skipLines
- 3.2.13 strict
- 3.2.14 beans
- 3.2.15 entity
- 3.2.16 createOn
- 3.2.17 element
- 3.2.18 expression -> assign | copy | with...as
- 3.2.19 format
- 3.2.20 keys -> keys
- 3.2.21 list
- 3.2.22 mapping -> map...to
- 3.2.23 lookup
- 3.2.24 marker
- 3.3 Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)
- 3.4 Annotations
- 3.5 Comments
- 3.6 Smooks (Extended)
- 3.7 WorkerThread (Runnable)
- 3.8 TriggerView & Executorservice
- 3.9 DSL Inferrer
- 3.10 DSL Scope Provider
- 3.11 DSL Proposal Provider
- 3.12 DSL Validator
Purpose
The Data Interchange DSL (datainterchange for short) is made for defining data exchange models that can be used to import data from various formats (CSV, XML, EDI, etc.), map the data to entities, store them into database, or export them back into other formats.
You only need to define the relationship between the file and the bean, not the import / export process themselves. Once defined, these models can be used in e.g. action DSL to define actions which, when triggered, execute the actual import / export process, which are generated automatically by the OSBP based on the model.
Overview
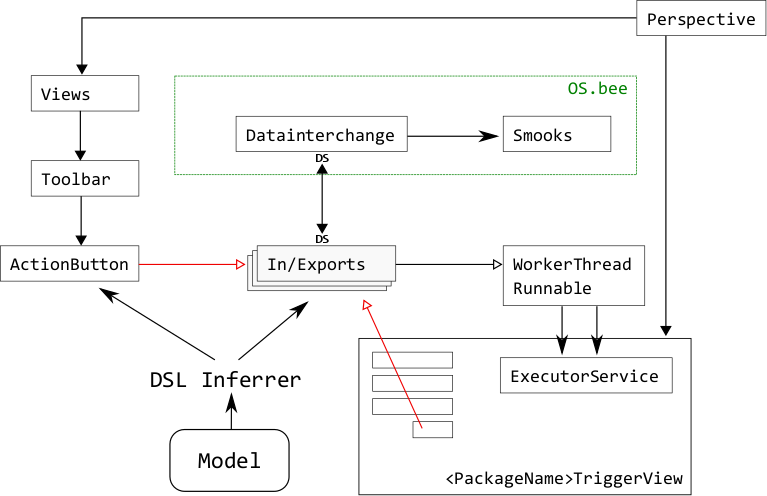
As shown in Figure 1, the DSL inferrer will generate various views and In/Export component according to model described by datainterchange DSL (and action DSL, in the case of ActionButtons). The action buttons, when clicked, will trigger their corresponding In/Export processes by putting WorkerThreadRunnable jobs into the executor job pool within the TriggerView (prefixed with datainterchang name), buttons (and toolbar / menus containing them) are further included in the perspective.
The main semantic elements of the Compex Data Interchange DSL are the following:
-
package
- - specify the datainterchange package, which acts as a namespace. It should have the form
net.osbee.sample.<applicationname>.datainterchangesby convention.
- - specify the datainterchange package, which acts as a namespace. It should have the form
- titletext
- - the name of the datainterchange package. This name will be used for code generation and should thus be unique if there are multiple datainterchange packages.
- interchangename
Data Interchange Model File
Datainterchange DSL model files end with the .data extension. Data Interchange models may be split into several .data files, as long as they have the same package declaration.
package net.osbee.sample.<applicationname>.datainterchanges title "<titletext>" {
interchange <interchangename> persist file
<fileformat> "<filepath>" [<further specifications>]
beans {
<entity relationships>
}
}
Package
Datainterchange DSL model files must start with a package declaration. Packages are the root element of the Entity DSL grammar. All interchange units have to be defined in the package.
Reserved Keywords
In the following we’ll dive deeper into the description and the usage of Datainterchange related and reserved keywords.
interchange
describedBy
merge
persist
remove
elementSize
file -> CSV | EDI | XML
report
delimiter
indent
quoteCharacter
skipLines
strict
beans
entity
createOn
element
expression -> assign | copy | with...as
format
keys -> keys
list
mapping -> map...to
lookup
marker
Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)
Annotations
Comments
Smooks (Extended)
just links???