Difference between revisions of "Datainterchange DSL"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A general introduction and some high-level concepts for | + | A general introduction and some high-level concepts for OSBP DSLs can be found in [[OSBP DSL Documentation]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Please note that you can only make use of the Datainterchange DSL by downloading its packages from the [http://dev.osbee.org/free-download/ download section] of our [http://dev.osbee.org/home/ website]. | ||
==Purpose== | ==Purpose== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
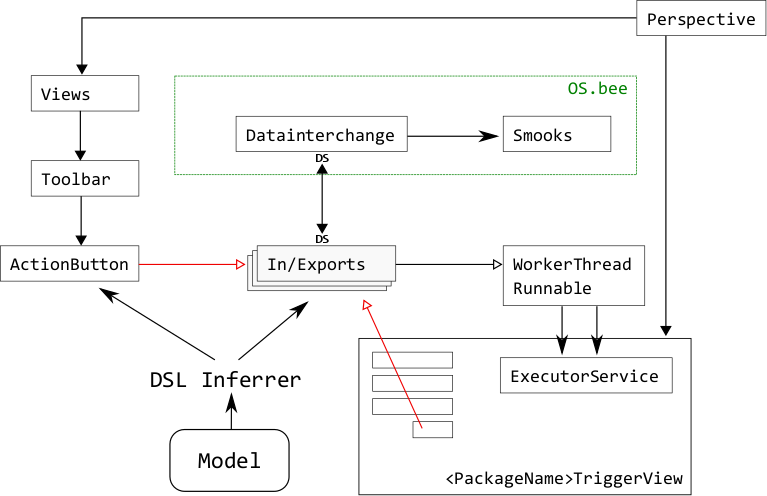
| − | [[File:Datainterchange.png|center|''Figure 1 - Data Interchange Structure.'']] | + | [[File:Datainterchange.png|center|frame|''Figure 1: - Data Interchange Structure.'']] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | As shown in Figure 1, the DSL inferrer will generate various views and In/Export component according to model described by datainterchange DSL (and action DSL, in the case of ActionButtons). The action buttons, when clicked, will trigger their corresponding In/Export processes by putting WorkerThreadRunnable jobs into the executor job pool within the TriggerView (prefixed with datainterchang name), buttons (and toolbar / menus containing them) are further included in the perspective. | ||
==Data Interchange Model File== | ==Data Interchange Model File== | ||
Datainterchange DSL model files end with the <code>.data</code> extension. Data Interchange models may be split into several <code>.data</code> files, as long as they have the same package declaration. | Datainterchange DSL model files end with the <code>.data</code> extension. Data Interchange models may be split into several <code>.data</code> files, as long as they have the same package declaration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Reserved Keywords=== | ||
| + | In the following we’ll dive deeper into the description and the usage of Datainterchange related and reserved keywords. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====import==== | ||
| + | In the import section are all entities to be found - as full qualified names – that are currently used in the DSL and automatically imported/added (OXImportDeclaration) by editing it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity1 | ||
| + | import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity2 | ||
| + | import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====package==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Datainterchange DSL model files must start with a package declaration. Packages are the root element of the DSL grammar and must be defined as follow package <PackageName> for example | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package net.osbee.sample.ApplicationName.datainterchanges { } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Data Interchange models may be split into several .data files, as long as they have the same package declaration. | ||
| + | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 57: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | ====titel==== | ||
| + | With the keyword title you can give a name to the corresponding TriggerView dialog inside your application. | ||
| + | For example the definition of the same datainterchanges package from above with the title DataInterchange | ||
| − | = | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> |
| − | + | package net.osbee.sample.foodmart.datainterchanges title "DataInterchange" {} | |
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | You can get more details about the TriggerView in the section below. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
====interchange==== | ====interchange==== | ||
| + | All interchange units have to be defined in the package followed by the Entity they are referencing/applied to. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> <FileFormat> {} | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
====describedBy==== | ====describedBy==== | ||
| + | With this keyword you get to set the optional description of an interchange unit as shown below. | ||
| − | = | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> |
| + | interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> describedBy "This is a description of the Datainterchange DSL Unit EntityName" … {} | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ====persist==== | + | ====persist, merge, remove==== |
| + | With those keywords defined inside the Enum Entity Manager Mode, you set how the data have to be process by inserting then into a database. | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> … {} | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Example 1: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge … {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Example 2: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit2 persist … {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Example 3: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit3 remove … {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====file==== |
| + | With the keyword file you are able to set the file format of the files you intent to process with you interchange unit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> file <FileNameFormat> {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The current supported file formats are CSV, EDI and XML followed by the name of the file you want to process, given its full path location in the system. | ||
| + | Example 1: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Example 2: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit2 persist file XML "C:/temp/testFile.xml” {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Example 3: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit3 merge file EDI "C:/temp/testFile.edi” {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
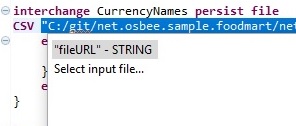
| + | After choosing the file format you can either give the file name as a String value in a double quote "..." as shown here above, or hold Ctrl+Space to get the option of opening a File Chooser/Picker to specify the file you want to work with. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:FileChooser.jpg|center|frame|''Figure 2: File Chooser'']] | ||
====elementSize==== | ====elementSize==== | ||
| + | With the keyword elementSize followed by a number between 0 and 100 ? you set the average size of the file (or set of data). | ||
| + | Example: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ====file | + | ====delimiter==== |
| + | With the keyword delimiter you set the delimiter/separation character of the file. | ||
| + | Example: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====skipLines==== | ||
| + | With the keyword skipLines followed by a number you specify the number of line to be skipped or not to be considered in the processing of the selected file. | ||
| + | Example: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" skipLines 1 {}</syntaxhighlight> | ||
====report==== | ====report==== | ||
| − | + | ||
====indent==== | ====indent==== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 126: | ||
====quoteCharacter==== | ====quoteCharacter==== | ||
| − | |||
====strict==== | ====strict==== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 132: | ||
====entity==== | ====entity==== | ||
| + | With the keyword '''entity''' you specify the Entity on what the interchange unit is based on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: <syntaxhighlight lang="java">interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" skipLines 1 { | ||
| + | entity SampleEntity1 … {} | ||
| + | }</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information about Entities you can review the corresponding [http://download.osbee.org/documentation/index.php/Entity_DSL#Entities Entity DSL documentation]. | ||
====createOn==== | ====createOn==== | ||
| Line 93: | Line 157: | ||
====marker==== | ====marker==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Enums== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Enums''' are an abstraction of the Java <code>enum</code>. They compile to <code>enum</code> classes and can be used as properties in entities and beans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Entity-18.png|center|frame|''Figure 3: Defining <code>enums</code> allows using them as variables in entities and beans.'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Datainterchange DSL provides 3 Enum types that can be used: ''PredefinedBeanEnum'', ''PredefinedBeanTypeEnum'', ''ProgessBarStyleEnum'' and the ''EntityManagerMode''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===PredefinedBeanEnum=== | ||
| + | Contains the definition of the values '''<code>now(NowDate) | start(StartDate) | UUID(UniversallyUniqueIdentifier)</code>''' used for ... | ||
| + | ===PredefinedBeanTypeEnum=== | ||
| + | Contains the definition of the values '''<code>Date(Date) | Millis(Milliseconds) | Nanos(Nanoseconds) | random(Random) | execContext(ExecuteContext)</code>''' used for ... | ||
| + | ===ProgessBarStyleEnum=== | ||
| + | Contains the definition of the values '''<code>none(none) | normal(normal) | important(important)</code>''' used for setting the style of a progressbar. | ||
| + | ===EntityManagerMode=== | ||
| + | Contains the definition of the values '''<code>persist(persist) | merge(merge) | remove(remove)</code>''' used for specifying the Entity Manager Mode in order to decide how to manage data inside a database before committing any changes. | ||
==Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)== | ==Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)== | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 4 August 2017
A general introduction and some high-level concepts for OSBP DSLs can be found in OSBP DSL Documentation.
Please note that you can only make use of the Datainterchange DSL by downloading its packages from the download section of our website.
Contents
- 1 Purpose
- 2 Overview
- 3 Data Interchange Model File
- 3.1 Reserved Keywords
- 3.1.1 import
- 3.1.2 package
- 3.1.3 titel
- 3.1.4 interchange
- 3.1.5 describedBy
- 3.1.6 persist, merge, remove
- 3.1.7 file
- 3.1.8 elementSize
- 3.1.9 delimiter
- 3.1.10 skipLines
- 3.1.11 report
- 3.1.12 indent
- 3.1.13 quoteCharacter
- 3.1.14 strict
- 3.1.15 beans
- 3.1.16 entity
- 3.1.17 createOn
- 3.1.18 element
- 3.1.19 expression -> assign | copy | with...as
- 3.1.20 format
- 3.1.21 keys -> key
- 3.1.22 list
- 3.1.23 mapping -> map...to
- 3.1.24 lookup
- 3.1.25 marker
- 3.1 Reserved Keywords
- 4 Enums
- 5 Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)
- 6 Annotations
- 7 Comments
- 8 Smooks (Extended)
- 9 WorkerThread (Runnable)
- 10 TriggerView & Executorservice
- 11 DSL Inferrer
- 12 DSL Scope Provider
- 13 DSL Proposal Provider
- 14 DSL Validator
- 15 Copyright Notice
Purpose
The Data Interchange DSL (datainterchange for short) is made for defining data exchange models that can be used to import data from various formats (CSV, XML, EDI, etc.), map the data to entities, store them into database, or export them back into other formats.
You only need to define the relationship between the file and the bean, not the import / export process themselves. Once defined, these models can be used in e.g. action DSL to define actions which, when triggered, execute the actual import / export process, which are generated automatically by the OSBP based on the model.
Overview
As shown in Figure 1, the DSL inferrer will generate various views and In/Export component according to model described by datainterchange DSL (and action DSL, in the case of ActionButtons). The action buttons, when clicked, will trigger their corresponding In/Export processes by putting WorkerThreadRunnable jobs into the executor job pool within the TriggerView (prefixed with datainterchang name), buttons (and toolbar / menus containing them) are further included in the perspective.
Data Interchange Model File
Datainterchange DSL model files end with the .data extension. Data Interchange models may be split into several .data files, as long as they have the same package declaration.
Reserved Keywords
In the following we’ll dive deeper into the description and the usage of Datainterchange related and reserved keywords.
import
In the import section are all entities to be found - as full qualified names – that are currently used in the DSL and automatically imported/added (OXImportDeclaration) by editing it.
import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity1
import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity2
import ns net.osbee.sample.<ApplicationName>.entities.SampleEntity3
package
Datainterchange DSL model files must start with a package declaration. Packages are the root element of the DSL grammar and must be defined as follow package <PackageName> for example
package net.osbee.sample.ApplicationName.datainterchanges { }
Data Interchange models may be split into several .data files, as long as they have the same package declaration.
package net.osbee.sample.<applicationname>.datainterchanges title "<titletext>" {
interchange <interchangename> persist file
<fileformat> "<filepath>" [<further specifications>]
beans {
<entity relationships>
}
}
titel
With the keyword title you can give a name to the corresponding TriggerView dialog inside your application. For example the definition of the same datainterchanges package from above with the title DataInterchange
package net.osbee.sample.foodmart.datainterchanges title "DataInterchange" {}
You can get more details about the TriggerView in the section below.
interchange
All interchange units have to be defined in the package followed by the Entity they are referencing/applied to.
interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> <FileFormat> {}
describedBy
With this keyword you get to set the optional description of an interchange unit as shown below.
interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> describedBy "This is a description of the Datainterchange DSL Unit EntityName" … {}
persist, merge, remove
With those keywords defined inside the Enum Entity Manager Mode, you set how the data have to be process by inserting then into a database.
interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> … {}
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge … {}
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit2 persist … {}
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit3 remove … {}
file
With the keyword file you are able to set the file format of the files you intent to process with you interchange unit.
interchange <SampleInterchangeUnitName> <EntityManagerMode> file <FileNameFormat> {}
The current supported file formats are CSV, EDI and XML followed by the name of the file you want to process, given its full path location in the system.
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” {}
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit2 persist file XML "C:/temp/testFile.xml” {}
interchange SampleInterchangeUnit3 merge file EDI "C:/temp/testFile.edi” {}
After choosing the file format you can either give the file name as a String value in a double quote "..." as shown here above, or hold Ctrl+Space to get the option of opening a File Chooser/Picker to specify the file you want to work with.
elementSize
With the keyword elementSize followed by a number between 0 and 100 ? you set the average size of the file (or set of data).
Example:interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” {}
delimiter
With the keyword delimiter you set the delimiter/separation character of the file.
Example:interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" {}
skipLines
With the keyword skipLines followed by a number you specify the number of line to be skipped or not to be considered in the processing of the selected file.
Example:interchange SampleInterchangeUnitName merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" skipLines 1 {}
report
indent
quoteCharacter
strict
beans
entity
With the keyword entity you specify the Entity on what the interchange unit is based on.
Example:interchange SampleInterchangeUnit1 merge elementSize 50 file CSV "C:/temp/testFile.csv” delimiter ";" skipLines 1 {
entity SampleEntity1 … {}
}
For more information about Entities you can review the corresponding Entity DSL documentation.
createOn
element
expression -> assign | copy | with...as
format
keys -> key
list
mapping -> map...to
lookup
marker
Enums
Enums are an abstraction of the Java enum. They compile to enum classes and can be used as properties in entities and beans.
The Datainterchange DSL provides 3 Enum types that can be used: PredefinedBeanEnum, PredefinedBeanTypeEnum, ProgessBarStyleEnum and the EntityManagerMode.
PredefinedBeanEnum
Contains the definition of the values now(NowDate) | start(StartDate) | UUID(UniversallyUniqueIdentifier) used for ...
PredefinedBeanTypeEnum
Contains the definition of the values Date(Date) | Millis(Milliseconds) | Nanos(Nanoseconds) | random(Random) | execContext(ExecuteContext) used for ...
ProgessBarStyleEnum
Contains the definition of the values none(none) | normal(normal) | important(important) used for setting the style of a progressbar.
EntityManagerMode
Contains the definition of the values persist(persist) | merge(merge) | remove(remove) used for specifying the Entity Manager Mode in order to decide how to manage data inside a database before committing any changes.
Configuration Settings / Smooks Framework (A small introduction)
Annotations
Comments
Smooks (Extended)
just links???
WorkerThread (Runnable)
TriggerView & Executorservice
DSL Inferrer
DSL Scope Provider
DSL Proposal Provider
DSL Validator
Copyright Notice
All rights are reserved by Compex Systemhaus GmbH. In particular, duplications, translations, microfilming, saving and processing in electronic systems are protected by copyright. Use of this manual is only authorized with the permission of Compex Systemhaus GmbH. Infringements of the law shall be punished in accordance with civil and penal laws. We have taken utmost care in putting together texts and images. Nevertheless, the possibility of errors cannot be completely ruled out. The Figures and information in this manual are only given as approximations unless expressly indicated as binding. Amendments to the manual due to amendments to the standard software remain reserved. Please note that the latest amendments to the manual can be accessed through our helpdesk at any time. The contractually agreed regulations of the licensing and maintenance of the standard software shall apply with regard to liability for any errors in the documentation. Guarantees, particularly guarantees of quality or durability can only be assumed for the manual insofar as its quality or durability are expressly stipulated as guaranteed. If you would like to make a suggestion, the Compex Team would be very pleased to hear from you.
(c) 2016-2025 Compex Systemhaus GmbH