Datatype DSL
Contents
Purpose
The Datatype DSL is, beside the Entity DSL, one of the most basic DSL for the Software Factory. It provides you with the most common used basic (atomic) datatypes by mapping them. It also allows you to define new simple and complex datatypes, to be used in all your projects. You will find here a couple of informations to help you understand how to use it.
Overview
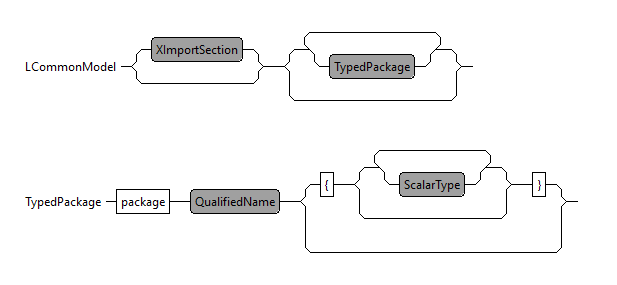
The main semantic elements of the Compex Datatype DSL are the following:
- "Import" declarations - used to import external Java classes.
- "Package" - the root element that contains all the other elements. A model can contain multiple packages.
- "Datatype" declarations - the way to define datatypes that can be used in entities and beans.
- "Enum" declarations - the abstraction for Java enums.
The Datatype DSL as such is working under the hood of your application's entity model by providing acces to datatypes (Number, String, Boolean...). The figure below represents straightforward how the grammar was designed in order to make it possible for you to use and also create your own datatypes. This is the structural foundation, on which the Datatype DSL model is based on.
Datatypes Model Files
Datatype DSL model files end with the .datatype extension. Datatype models may be split into several .datatype files, as long as they have the same package declaration.
Reserved Keywords
In the following we will dive deeper into the description and the usage of datatype related and reserved keywords.
package
Datatype model files must start with a package declaration. Packages are the root element of the Datatype DSL grammar. Everything is contained in a package: Datatypes and Enums have to be defined inside the Package definition. One document can contain multiple packages with unique names.
import importStatement package name { datatype datatypeDefinition enums enumDefinition }
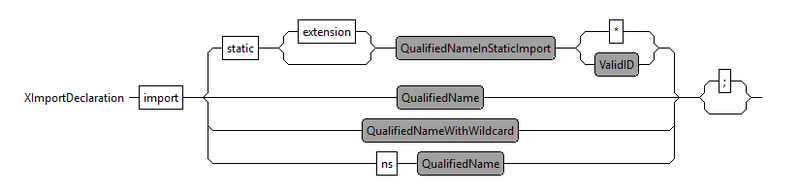
import
Although Import-Statements are located above the package declaration, they are optional as you may not necessarely need to reference any external Java Classes to extend the your datatype definitions. Using an import statement is a way to make these elements available in the current namespace without having to address them by their fully qualified name.
Import statements allow the use of the '*' wildcard.
import importStatement
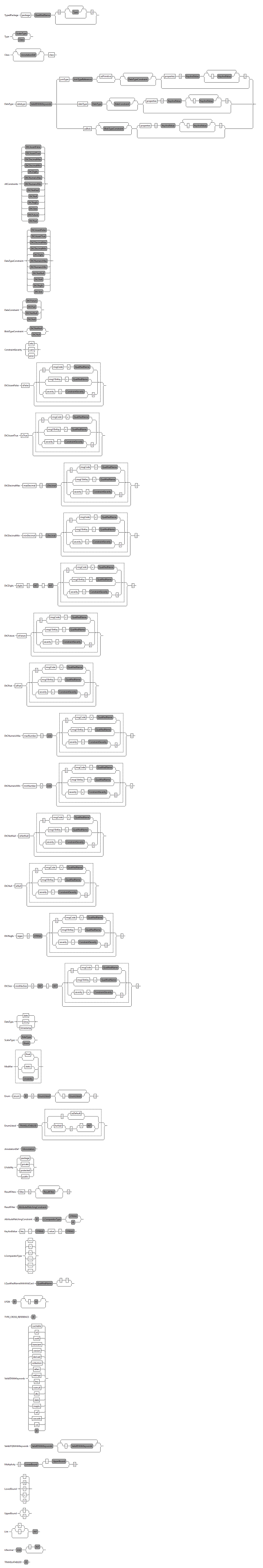
datatype
The Datatype DSL allows the definition of datatypes. These are translated by the inferrer into their standard Java representation. The behavior of the generator can be controlled by the datatype definitions. Datatypes defined in an .datatype file are local to that file.
There are three types of datatype definitions:
jvmType
Datatype definitons that map types to jvmType take the basic syntax of
datatype <name> jvmType <type> asPrimitive
Specifying datatypes in this manner uses an appropriate wrapper class in the generated Java code; adding the keywords asPrimitive enforces the use of primitive datatypes where applicable:
Example 1:
datatype foo jvmType Integer
compiles to an Integer whereas
Example 2:
datatype foo jvmType Integer asPrimitive
results in int.
Example 3:
datatype boolean jvmType java.lang.Boolean asPrimitive datatype short jvmType java.lang.Short asPrimitive datatype int jvmType java.lang.Integer asPrimitive datatype long jvmType java.lang.Long asPrimitive datatype double jvmType java.lang.Double asPrimitive datatype character jvmType java.lang.Character asPrimitive datatype byte jvmType java.lang.Byte asPrimitive datatype Boolean jvmType java.lang.Boolean datatype Short jvmType java.lang.Short datatype Int jvmType java.lang.Integer datatype Long jvmType java.lang.Long datatype Double jvmType java.lang.Double datatype Character jvmType java.lang.Character datatype Byte jvmType java.lang.Byte datatype BigDecimal jvmType java.math.BigDecimal datatype String jvmType java.lang.String
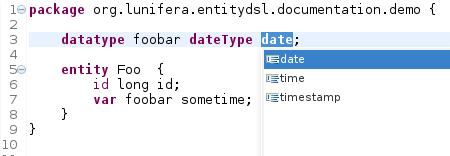
dateType
The datatypes for handling temporal information can be defined by the following statement:
datatype <name> dateType {date|time|timestamp} [options]*
Datatypes that have been defined in this manner can be used as property variables in entities and beans.
Example 1:
datatype MyDate dateType date
Example 2:
datatype MyDate dateType time
Example 3:
datatype MyDate dateType timestamp
You can also extend or constraint the datetype definition by adding one or more of the following options:
[options]: <isPast> specifies that every object of this datetype can only accept value prior its creation. <isFuture> specifies that every object of this datetype can only accept value after its creation. <isNull> specifies that any object of this datetype can have the value null. <isNotNull> specifies that the every object of this datetype can not have the value null. <'['severity = {error|info|warn} ']'> sets the severity level of a non valid value.
Please note that setting the severity level has the effect of showing context based information
(here non valid data) in the UI on the corresponding field by displaying either a red exclamation point(error)
or a small yellow triangle(info) or blue triangle(info). This depends of course on the set of options you would
have chosen in your datetype definition.
Example 4:
datatype BirthDate dateType date isNotNull isPast[severity=error]
asBlob
Binary blobs can be handled by defining a datatype with the asBlob keywords. The Java implementation of such a blob is a byte array. Appropriate persistence annotations are automatically added.
datatype <name> asBlobFile:DatatypeBlob.pngFigure 9: Including binary blobs by using a datatype with theasBlobkeywords
enum
Enumerations can be handled by defining a slightly different datatype with the enum keywords. The Java implementation of such a enum is exactly the same.
enum <name> { <Value1> [, <Value2>]* }
Example:
enum LayoutingStrategies { Form2, Form3, Horizontal, Vertical, Grid, Css } enum ItemClassification { Class_A, Class_B, Class_C }
enum keyword.
properties
With the properties keyword you are able to influence the visualization of UI components in extending the datatype definitions with additional metadata.
The properties take effect whenever the data type is used in entity models, which are respectivelyinherited DTO DSL models. Changes on the datatype property therefore effect all visualizations depending on this datatype.
All these properties are required to achieve different behaviour on the visualization of information.
Some of them are used by the AutowireHelper, other are used by the AbstractLayoutingStrategy to create varying ui elements based on the same data type.
Properties are a set of definitions each consisting of a pair of terms called key and value. A name–value pair, key–value pair, field–value pair or attribute–value pair is a fundamental data representation in computing systems and applications. Designers often desire an open-ended data structure that allows for future extension without modifying existing code or data. In such situations, all or part of the data model may be expressed as a collection of tuples <attribute name, value>; each element is an attribute–value pair. Depending on the particular application and the implementation chosen by programmers, attribute names may or may not be unique.
properties '(' key="AKey" value="AValue" [, key="AnotherKey" value="AnotherValue"]* ')'
Example
key=age value=15 key=name value=Joe
Please note that in this context the key is case-insensitive whereas the value is not. Key and value are always enclosed by quotation marks.
Textareas
Let's consider the UI element know as Textarea. The key is textarea and the value determines the number of rows that will be created. The datatype is String.
Within a Sample application you will probably find:
in [projectname].datatypes:
datatype TextArea jvmType java.lang.String properties(key = "textarea" value = "5")
in [projectname].entitymodel:
var TextArea description
This construct creates a new datatype for project [projectname] which can be used in entitymodels, defining a textarea with 5 rows.
Images of a specified resolution
For performance reasons, images are stored in the database as base64 encoded strings. If uploaded, all resolutions defined in the blob-model are calculated and the resulting variants are stored in the database. As images are more often retrieved from database as stored, this approach helps the performance with the cost of an increased database storage space.
The key is blob and the value determines the resolution that will be created. The datatype is String.
Within a Sample application you will probably find:
in *.datatypes:
datatype SmartImagejvmType java.lang.String properties(key="Blob" value="2")
in *.entitymodel:
/** portrait of person */ var SmartImage portrait
Monetary and other decimal fields
To display fields formatted in a specified way there is the following construction: The key is decimalformat and the value determines the format pattern that will be created. The datatype is Double.
Please note that Float is no longer supported in this context.
To display a double value with preceding currency sign, you could use this sample:
datatype Price jvmType java.lang.Double as primitive properties (key="decimalformat" value="¤ ###,###.##")
Note that ¤ the ASCII character 164 can be HTML encoded to avoid codepage problems in your editor. This also works for all other special characters.
datatype Price jvmType java.lang.Double as primitive properties (key="decimalformat" value="¤ ###,###.##")
The format pattern has a variety of features designed to make it possible to format numbers in any locale, including support for Western, Arabic, and Indic digits. It also supports different kinds of numbers, including integers (123), fixed-point numbers (123.4), scientific notation (1.23E4), percentages (12%), and currency amounts ($123). All of these can be localized.
A decimalformat comprises a pattern and a set of symbols.
=Patterns=
Patterns have the following syntax:
Pattern: </br>PositivePattern PositivePattern ; NegativePattern
PositivePattern: </br>Prefixopt Number Suffixopt
NegativePattern: </br>Prefixopt Number Suffixopt
Prefix: any Unicode characters except \uFFFE, \uFFFF, and special characters
Suffix: any Unicode characters except \uFFFE, \uFFFF, and special characters
Number: Integer Exponentopt Integer . Fraction Exponentopt
Integer: MinimumInteger # # Integer # , Integer
MinimumInteger: 0 0 MinimumInteger 0 , MinimumInteger
Fraction: MinimumFractionopt OptionalFractionopt
MinimumFraction: 0 MinimumFractionopt
OptionalFraction: # OptionalFractionopt
Exponent: E MinimumExponent
MinimumExponent:
0 MinimumExponentopt
A decimalformat pattern contains a positive and negative subpattern, for example, "#,##0.00;(#,##0.00)". Each subpattern has a prefix, numeric part, and suffix. The negative subpattern is optional; if absent, then the positive subpattern prefixed with the localized minus sign ('-' in most locales) is used as the negative subpattern. That is, "0.00" alone is equivalent to "0.00;-0.00". If there is an explicit negative subpattern, it serves only to specify the negative prefix and suffix; the number of digits, minimal digits, and other characteristics are all the same as the positive pattern. That means that "#,##0.0#;(#)" produces precisely the same behavior as "#,##0.0#;(#,##0.0#)".
The prefixes, suffixes, and various symbols used for infinity, digits, thousands separators, decimal separators, etc. may be set to arbitrary values, and they will appear properly during formatting. However, care must be taken that the symbols and strings do not conflict. For example, either the positive and negative prefixes or the suffixes must be distinct to be able to distinguish positive from negative values. (If they are identical, then decimalformat will behave as if no negative subpattern was specified.) Another example is that the decimal separator and thousands separator should be distinct characters.
The grouping separator is commonly used for thousands, but in some countries it separates ten-thousands. The grouping size is a constant number of digits between the grouping characters, such as 3 for 100,000,000 or 4 for 1,0000,0000. If you supply a pattern with multiple grouping characters, the interval between the last one and the end of the integer is the one that is used. So "#,##,###,####" == "######,####" == "##,####,####".
=Special Pattern Characters=
Many characters in a pattern are taken literally; they are matched during parsing and output unchanged during formatting. Special characters, on the other hand, stand for other characters, strings, or classes of characters. They must be quoted, unless noted otherwise, if they are to appear in the prefix or suffix as literals.
The characters listed here are used in non-localized patterns. Localized patterns use the corresponding characters instead, and these characters lose their special status. Two exceptions are the currency sign and quote, which are not localized. In OS.bee you can use the HTML encoded name instead to avoid codepage problems.
| Symbol | HTML encoded | Location | Localized? | Meaning |
| 0 | 0 | Number | Yes | Digit |
| # | # | Number | Yes | Digit, zero shows as absent |
| . | . | Number | Yes | Decimal separator or monetary decimal separator |
| - | - | Number | Yes | Minus sign |
| , | , | Number | Yes | Grouping separator |
| E | E | Number | Yes | Separates mantissa and exponent in scientific notation. Need not be quoted in prefix or suffix. |
| ; | ; | Subpattern boundary | Yes | Separates positive and negative subpatterns |
| % | % | Prefix or suffix | Yes | Multiply by 100 and show as percentage |
| \u2030 | ‰ | Prefix or suffix | Yes | Multiply by 1000 and show as per mille value |
| ¤ (\u00A4) | ¤ | Prefix or suffix | No | Currency sign, replaced by currency symbol. If doubled, replaced by international currency symbol. If present in a pattern, the monetary decimal separator is used instead of the decimal separator. |
| ' | ' | Prefix or suffix | No | Used to quote special characters in a prefix or suffix, for example, "'#'#" formats 123 to "#123". To create a single quote itself, use two in a row: "# oclock". |
- Date and time fields:
To display defined fractions of a date and time value you can use the following construct:
The key is date, time or date_time. The value determines the resolution that will be created. The datatype is Date.
If the key is date, then the time fraction of the Date datatype will be omitted. If the key is time, then the date fraction of the Date datatype will be omitted. If the key is date_time, then all parts are displayed.
The value represents the resolution of the respective key. All components of the resolution pattern (divided by dots) are arranged in the order of the currently selected locale. Some resolutions only make sense with the appropriate key. E.g. with the key date, the resolution SECOND is not working. Resolutions are following a coarse-to-fine sequence and must be used in capitals:
| value | resolution pattern | meaning |
| YEAR | yyyy | only display the 4 digit year |
| MONTH | yyyy.MM | display year and month |
| DAY | yyyy.MM.dd | display day month and year |
| HOUR | yyyy.MM.dd HH | complete date with hour |
| MINUTE | yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm | complete date with hour and minute |
| SECOND | yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss | complete date and time |
Custom Datatypes
In this section you will find some informations about the available custom datatypes (OSBEE).
BlobMapping
This is a custom datatypes that allows the use of big data as blob.
Example 1:
datatype BlobMapping jvmType java.lang.String
properties (
key="Blob" value="2"
/**
* value="0" name="unnormalized" resolution="unknown"
* value="1" name="small" resolution="16x16"
* value="2" name="mid" resolution="64x64"
* value="3" name="portrait" resolution="64x128"
* value="4" name="landscape" resolution="128x64"
* value="5" name="big" resolution="200x-1"
*
*/
);
Example 2:
Disclaimer / Notice
You have created several new datatypes from scratch or defined some by referencing already existing Java classes.
One of the logical next steps would be to make use of them inside your project as it is similarly done within the Entity DSL Model with import-statements.
Copyright Notice
All rights are reserved by Compex Systemhaus GmbH. In particular, duplications, translations, microfilming, saving and processing in electronic systems are protected by copyright. Use of this manual is only authorized with the permission of Compex Systemhaus GmbH. Infringements of the law shall be punished in accordance with civil and penal laws. We have taken utmost care in putting together texts and images. Nevertheless, the possibility of errors cannot be completely ruled out. The Figures and information in this manual are only given as approximations unless expressly indicated as binding. Amendments to the manual due to amendments to the standard software remain reserved. Please note that the latest amendments to the manual can be accessed through our helpdesk at any time. The contractually agreed regulations of the licensing and maintenance of the standard software shall apply with regard to liability for any errors in the documentation. Guarantees, particularly guarantees of quality or durability can only be assumed for the manual insofar as its quality or durability are expressly stipulated as guaranteed. If you would like to make a suggestion, the Compex Team would be very pleased to hear from you.
(c) 2016-2025 Compex Systemhaus GmbH