OS.bee Tutorial
Contents
OS.bee Tutorial
Introduction
This tutorial will introduce the architecture, technology and functionality of OS.bee using basic OS.bee application My1App.
My1App is a personal administration application consisting of a collection of models based on OS.bee Domain Specific Languages. It is generated by Eclipse wizards; the wizards build the Eclipse workspace, provide the basic structure and a number of consistent objects of models.
We use the "2BEE concept":
- describe the requirements from the point of a fictive user with using story map
- technically implement the requirements of user
You can step by step expand the rudimentary person administration (which has only basic configuration) with the user stories described in the story map, and then generate an employee administration based on your new person administration.
Please notice:
- The task solutions can often be solved either by DSL code or graphic modeling. We will only present the solution with DSL code in this tutorial. You can use any one of them as you will.
- Each tutorial user stories are independent from each other; you don’t need to totally complete the tutorial in once.
Purpose
The task for the user of this tutorial is first the administration of personal data and then the main task is the administration of employee data.
Requirement
My1App is a personal administration application consisting of a collection of models based on OS.bee Domain Specific Languages. It is generated by Eclipse wizards; the wizards build the Eclipse workspace, provide the basic structure and a number of consistent objects of models. So before executing the tutorial steps in this tutorial using My1App, the appropriate wizards must be installed. You can find more information about installation in doc of My1App.
My1App has the following basic objects:
- The superclass BaseID, which has only one attribute identifier (id) as UUID (See UUID). It is the technical key as a basis of identification and it is an obligation for all entities.
- The entity Person , which inherits the identifier attribute (id) from the superclass BaseID and has additional personal attributes.
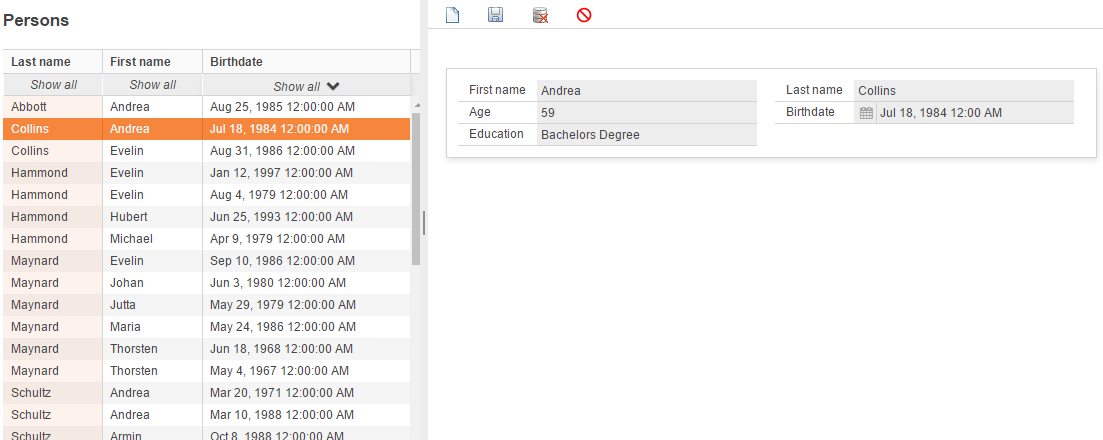
The following vertically divided person-view represent the entity Person in My1App, on the left side is the Person-Table and on the right side is the Person-Dialog:
Use cases
The personal administration should be extended by the following use cases:
- change address
- search person with full-name
- establish current age of person
- add profile picture
- add gender
- add marital status
The expected employee administration is described by the following use cases:
- hire employee
- fire employee
- increase salary of employee
- assign employee
- transfer employee
- evaluate employee
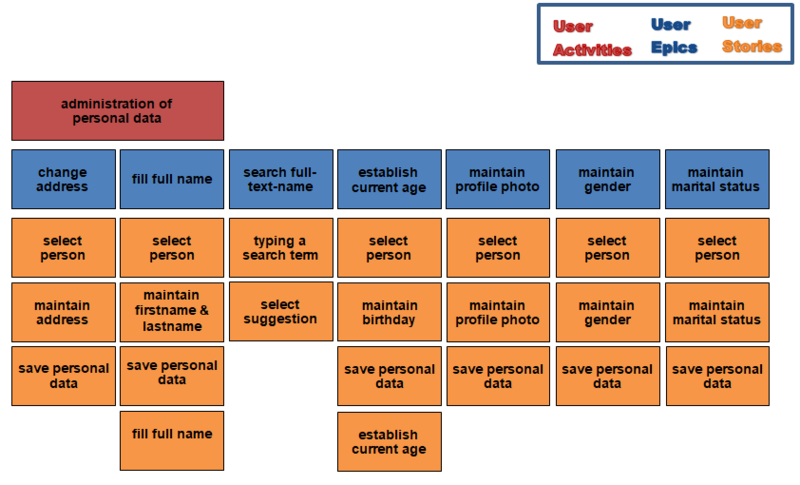
Story map
User stories
Administration of personal data
Change the address
Target:
Introducing the EntityDSL instance by extending an existing entity with new attributes.
Requirement:
As an administrator, I want to change a person's address.
Process:
To change the address of a person, we need to set Street(Person.street), City(Person.city), Postal Code(Person.postal_code) and Country(Person.country) of a person. These are new attributes for the entity person(Person).
- Create the new attributes: street(street), city(city), postal code(postal_code) and country(country) as an extension of the entity person(Person).
search person with full-name
Establish current age
Add profile photo
Add gender
Add marital status
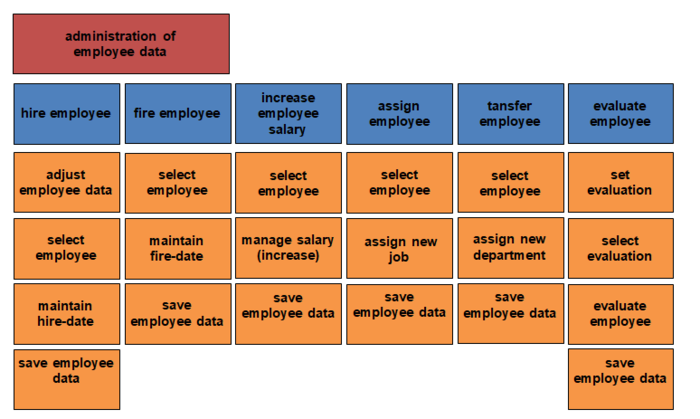
Administration of employee data
Create new entity of employee
Hire employee
Fire employee
Increase salary of employee
Assign employee
Transfer employee
Evaluate employee
Copyright Notice
All rights are reserved by Compex Systemhaus GmbH. In particular, duplications, translations, microfilming, saving and processing in electronic systems are protected by copyright. Use of this manual is only authorized with the permission of Compex Systemhaus GmbH. Infringements of the law shall be punished in accordance with civil and penal laws. We have taken utmost care in putting together texts and images. Nevertheless, the possibility of errors cannot be completely ruled out. The Figures and information in this manual are only given as approximations unless expressly indicated as binding. Amendments to the manual due to amendments to the standard software remain reserved. Please note that the latest amendments to the manual can be accessed through our helpdesk at any time. The contractually agreed regulations of the licensing and maintenance of the standard software shall apply with regard to liability for any errors in the documentation. Guarantees, particularly guarantees of quality or durability can only be assumed for the manual insofar as its quality or durability are expressly stipulated as guaranteed. If you would like to make a suggestion, the Compex Team would be very pleased to hear from you.
(c) 2016-2026 Compex Systemhaus GmbH